Blockchain + Supply Chain Financial Depth Research Report
Welcome global investment banks, VCs, PEs, mergers and acquisitions, funds, brokerages, trusts, banks, insurance, leasing, investment and other financial giants to pay attention to the first brand of China Investment Bank - China Investment Bank Club, looking for quality projects, funds and access to the world's top financial layer Please contact: IBC-Super Assistant (IBC-service, add WeChat, please specify: Region-Enterprise-Position-Name) Share: All the big coffees please share articles to the circle of friends; Follow: After watching, see more, history news is more exciting Pay attention to the "China Investment Bank Club" or find the micro-signal "ibankclub". After paying attention, you can reply to your direction of concern (we will post heavyweight articles according to your needs).
|
Since the blockchain boom in China in 2016, the entire industry has been constantly exploring various types of landing scenes. It is really so much a blockchain that attracts countless entrepreneurs to compete. So what are the advantages of the supply chain finance track? What are the pain points of the traditional model? What new business models can the blockchain create to solve these problems? How do startups cut into this field?
|
Research Report: Blockchain + Supply Chain Finance | Distributed Capital
Moody's, the world's leading bond rating agency, has given 127 blockchain cases, from points to transaction clearing, from document deposit to supply chain management, from cross-border payments to supply chain finance. Among such a large number of applications, the supply chain finance sector has attracted much attention, and commercialization has progressed rapidly.
This is because, first of all, the supply chain finance scenario has a trillion-level market scale, and the ceiling is high enough. Secondly, this scenario naturally requires multi-party cooperation, but there is no traditional centralized organization in governance, which needs to be built with a blockchain. Trust, at the same time, technically this scenario does not require high concurrency, and current blockchain technology can satisfy.
So what are the advantages of the supply chain finance circuit, what are the pain points of the traditional model, and what new business models can be created by the blockchain to solve these problems, and how the startups have cut into this field, and the industry already has Which cases, as VC funds invested in more than 40 blockchain startups around the world, distributed capital will continue to pay attention to the application in this field.
First, the supply chain finance trillion-level market
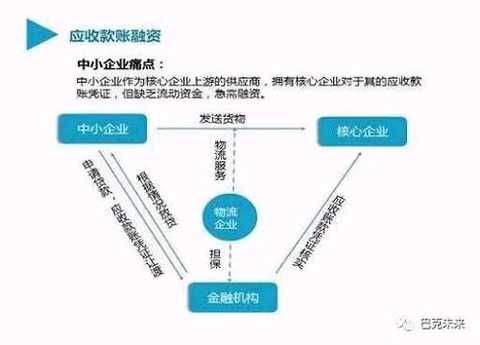
Supply Chain Finance (Supply ChainFinance): refers to the core enterprises in the supply chain and its related upstream and downstream enterprises as a whole, relying on the core enterprises, using real-time trade as the premise, using self-compensated trade financing, Comprehensive financial products and services provided to upstream and downstream companies in the supply chain.
According to different financing collaterals, financial institutions divide supply chain finance into accounts receivable, prepaid and inventory financing, of which the size of accounts receivable is particularly large.
According to the National Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2016, China's industrial enterprises above designated size accounted for 12.6 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10%, which generated huge financing needs of enterprises. Compared with the huge accounts receivable, the annual commercial factoring capacity in China is only about 200 billion yuan in 2015. It can be seen that there is still a large amount of supply chain demand that has not been met, so the development of the supply chain financial industry is huge.
Second, how to solve the pain point of supply chain finance in blockchain
Pain point 1: SME financing difficulties in the supply chain, high cost
Since the bank relies on the core enterprise's ability to control the goods and adjust the sales ability, for the sake of risk control, the bank is only willing to provide factoring services to the upstream suppliers (limited to the first-tier suppliers) that have direct accounts payable obligations to the core enterprises. Or provide advance payment or inventory financing to its downstream distributor (primary supplier).
This has led to the unsatisfied demand of secondary and tertiary suppliers/distributors with huge financing needs, the limited volume of supply chain finance, and the lack of timely financing for SMEs, which may lead to product quality problems. Will hurt the entire supply chain system.
Blockchain solution:
We issue it on the blockchain and run a digital ticket that can be randomly split and transferred in an open, transparent, multi-party testimony.
This model is equivalent to making the credit in the entire commercial system become conductive and traceable, providing financing opportunities for a large number of SMEs that could not be financed, greatly improving the efficiency and flexibility of bill circulation, and reducing the funds of SMEs. cost.
According to statistics, in the past, traditional supply chain financial companies could only provide financing services to 15% of supply chain suppliers (small and medium enterprises). After using blockchain technology, 85% of suppliers can enjoy it. Financing convenience.
Pain point 2. As the main financing tool for supply chain finance, the current use of commercial drafts and bank drafts is limited, and the transfer is difficult.
The use of commercial bills is subject to the credibility of the company, and it is difficult to control the timing of the discount of bank drafts. At the same time, it is not difficult to transfer these bonds.
Because in the actual financial operation, the bank is very concerned about the legal effect of the “transfer notice†of the accounts receivable claims. If the core enterprise cannot sign back, the bank will not be willing to grant credit. It is understood that the bank is very cautious about the legal effect of signing the "transfer notice" of this credit, and even requires the legal representative of the core enterprise to sign the bank in person. Obviously, this method is extremely difficult to operate.
Blockchain solution:
Banks and core enterprises can build a chain of alliances, which can be used by all member companies in the supply chain. The use of multi-party signatures and non-tamperable features of blockchains can lead to multi-party consensus on debt transfer and reduce operational difficulty.
Of course, the system design should be able to achieve the legal notice effect of bond transfer. At the same time, the bank can also trace the transactions of each node and outline the transaction flow chart.
Pain point 3: Supply chain financial platform / core enterprise system is difficult to self-certify innocence, resulting in high cost of capital control costs
In the current supply chain financial business, in addition to worrying about the repayment ability and repayment willingness of the company, the bank or other funds are also concerned about the authenticity of the transaction information itself, and the transaction information is recorded by the ERP system of the core enterprise.
Although the ERP tampering is difficult, it is not absolutely credible. The bank is still worried that the core enterprises and suppliers/distributors will collude with the modification information. Therefore, it is necessary to invest human and material resources to verify the authenticity of the transaction, which increases the cost of additional control.
Blockchain solution:
As a "trusted machine", the blockchain has the characteristics of traceability, consensus and decentralization, and the data on the blockchain is time-stamped. Even if the data of a node is modified, it cannot be covered. Therefore, the blockchain can provide an absolutely credible environment, reduce the cost of risk control at the fund end, and solve the bank's doubts about being tampered by information.
3. How should blockchain companies cut into supply chain finance?
In terms of market selection, we believe that blockchain startups should choose segments with high ceilings, such as home appliances, automotive zeros, clothing, and pharmaceuticals. On the one hand, these industries have a broad market, on the other hand, their supply chain management infrastructure is relatively complete, and the upfront cost of the upper blockchain is small.
We believe that there are two modes in which blockchain companies cut into supply chain finance.
The first is to directly cooperate with the core enterprise/platform to provide the underlying solution of the blockchain. After accumulating enough data, the docking chain will provide financial services to the connected parties. (Alliance Chain Mode)
In view of the fact that the blockchain itself cannot solve the problem of risk control, the enterprise-level risk control needs to revolve around the strong core enterprise at the present stage. At the same time, the support of the core enterprise can also effectively solve the problem of getting customers, because a large core enterprise generally There will be thousands of suppliers of various types.
At present, the domestic blockchain companies cut into the core enterprises including Bubi, Net recorded technology, etc., Bubi has launched a chain of alliances for the supply chain finance "Bunuo", the bank, core enterprises, factoring company When they are all linked, Buno is based in Guangzhou and Shenzhen, radiating business in the southeast region, and digging deep into the supply chain finance sector. It has previously signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Handan Iron and Steel.
The second model is to provide supply chain management services, such as traceability, tracking, visualization, etc., to integrate information flow, logistics and capital flow, and to engage in financial services on this basis. (private chain mode)
This mode is equivalent to building an application scenario with a blockchain. Just like the Alipay of the year, if Ma Yun did the Alipay directly, it would be difficult to do it. Because there is no application scenario, the Taobao that serves the real economy is first made. After Taobao, Alipay appeared as a centralized trust scene, and other applications were grafted on Alipay, which made ant Jinfu.
At present, in the domestic blockchain companies, the supply chain service model includes BITSE and food superiority.
For example, VeChain provides a method for anti-counterfeiting. By implanting an NFC chip for each product, the product is registered on the blockchain to have a digital identity, and then all the digital identities are recorded through the jointly maintained books. Information to achieve verification results. At present, Vechain products have been connected to more than 10 industry benchmark customers, and millions of IDs are running on the chain.
Four or three steps, aiming to build a supply chain financial exchange
From the perspective of the implementation path, the application of the blockchain in the supply chain finance field can be achieved in three steps.
As a premise, we need to first build a blockchain + supply chain finance alliance, the participants of the alliance include supply chain financial platform, core enterprises, professional financial intermediaries, capital parties, factoring institutions.
Each participant is required to undertake corresponding obligations. For example, the platform is responsible for providing supply chain information, customer information, and similar basic services for hydropower. The core enterprise understands the state of the industry and has control over the enterprises in the supply chain and is responsible for risk control.
Professional financial intermediaries can integrate platform information and provide customized supply chain financial products, such as personalized blockchain electronic bills. The fund side includes banks, Internet financial institutions and other customers responsible for docking corresponding risk preferences.
Once the alliance chain is set up, you can start a three-step strategy.
The first step is to put the data in the supply chain alliance on the chain, use the characteristics of the blockchain to make it impossible to tamper with, and provide data confirmation, traceability and other services.
In the second step, the assets are digitized, and the warehouse receipts, contracts, and blockchain notes that can represent financing needs are all turned into digital assets, and have the characteristics of being unique, non-tamperable, and non-replicable.
The third step, the trading of digital assets, the supply chain financial platform will be transformed into a financial asset exchange, the non-standard corporate loan demand will be transformed into standardized financial products, tokenization, docking investment and financing needs, value trading.
In the end, blockchain technology will effectively enhance the liquidity of supply chain financial assets, mobilize new financing tools and risk control systems to help cover the long tail market of SME financing, and promote supply chain finance as a service.
1. What is supply chain finance?
Supply chain finance is not a new thing. In fact, traditional financial institutions have been doing this – financing companies. Since both parties to the transaction are individuals, it is difficult to create a trust relationship with each other, which in turn leads to huge "credit costs." Because of this mistrust, it is difficult to make real-time transaction delivery. For example, a company and a supplier signing a partnership must have a one to six month billing period, and it is impossible to pay by cash. In order to provide driving capital for production, suppliers have to go to bank loans and pay interest for this, thereby increasing production costs.
|
At the same time, it is difficult for many industries to get loans from banks. In the case of the coal logistics industry, banks may not be willing to lend to coal logistics companies. Their collateral can only be coal. Based on the characteristics of this industry, it is difficult for banks to accurately assess the value of collateral and the overall risk tolerance is limited. It is difficult for large enterprises, and SMEs are less likely to get money from banks. Either collateral is required, or credit endorsement is required. SMEs have to go through five levels to meet the bank's hard requirements and get loans. The real economy needs to be produced as a lubricant.
Supply chain finance attempts to solve the problem of capital flow in a new way. The traditional bank's loan method is collateral, and the collateral is the transaction vouchers such as accounts receivable or bills in supply chain finance. In the industrial chain, there are often multiple blocking points where funds are not circulating. For example, a large company and a supplier signed a purchase contract of 2 million, and the contract stipulated that the payment was made in full within six months. These six months are the account period.
Second, if the supplier encounters difficulties and needs capital turnover, what should I do?
The game of supply chain finance is to take the six months of accounts receivable as collateral and take financial institutions to borrow money. Of course, suppliers need to pay a certain amount of interest in advance to get the money, 2 million may only get 1.8 million, and the remaining 200,000 interest. After 6 months, the big company no longer paid the supplier, but settled the payment of 2 million to the financial institution, and the financial institution made a profit of 200,000. This is the core logic of supply chain finance – trying to break through all the unobstructed blocking points of the traditional industry chain and let all the funds on the chain flow.
On May 11th, the “2016 Internet + Supply Chain Finance Research Report†released by NetEase Tianyan predicted that China's supply chain financial market will reach 15 trillion yuan in 2020, which is a very huge market.
Third, the main challenges of supply chain finance
First, the development of supply chain finance companies is subject to the low transparency of the entire supply chain industry.
The supply chain represents all the links involved in the production and distribution of goods, from raw materials to finished products to circulation to consumers. The current supply chain can cover hundreds of stages across dozens of geographic areas, making it difficult to track events or investigate incidents. Buyers lack a reliable way to verify and validate the true value of products and services because of the general lack of transparency in the supply chain, which means that the prices we pay do not accurately reflect the true cost of the product.
Second, the high transaction costs.
Taking the account receivables as the example, from the perspective of explicitness, the traditional supply chain financial chain involves multi-party processing of accounts payers, credit agencies, and factoring institutions, which takes a long time and costs. Since it is necessary for the trust organization to complete the corresponding certification and accounting processing, it usually takes at least several weeks to get the account, and the procedure is expensive. From a stealth perspective, in order to obtain a receivable, the trading company usually conducts a large amount of research and conducts risk control on this basis. If the amount of the target is too small, the interest will not cover the cost.
Third, the "magic" of the core enterprise.
The emergence and superposition of the above problems have prompted core companies to enter the historical arena. Just like the dam between the upstream and downstream, the core enterprise plays a role throughout the industrial chain. For core companies, they have the advantage of being engaged in supply chain finance. The core company has almost all the transaction data of all upstream and downstream enterprises, and holds all the accounts receivable and accounts payable at hand, and it has both good and bad. For example, Haier Group, Dixon and other industry giants have set up their own supply chain finance companies, and tried to use the Internet to improve efficiency and transform the industry.
|
Currently, the core business model is the main mode of supply chain finance. Core enterprises have positive significance in the development of supply chain finance. However, with the continuous development and growth of core enterprises, the wheel of history is repeated again. Advanced productivity will eventually become a stumbling block to progress. The existence of core enterprises will also limit the platform enterprises. development of. This is because the core enterprises are the most important roles in supply chain finance. Their voice and bargaining power are very strong, which will cause many platform-type supply chain finances to encounter a kind of paralysis: the core enterprises and their cooperation, soon You will see the benefits of supply chain finance, and then think of "why can I do this on my own?" So, the cooperation was lifted, and the self-built team and personal operation began.
Therefore, many platforms prefer to abandon industry giants and work with small companies or factoring companies. The "magic" of the core enterprises has smashed the development of many platforms. The core enterprise model can only be used in its own industry, or even can only make a fuss about its own industrial chain, the ceiling is too low. In addition, the possibility of joint fraud can also occur with the core enterprise model.
Fourth, the blockchain will reshape the supply chain financial model
Since the blockchain was proposed, the technology has rapidly spread from the niche topics in the geek circle to the innovation technology widely concerned by the academic community and the public, and has become the most dazzling star in Fintech. According to the latest release of Venture Scanner, the venture capital attracted by the blockchain sector has soared from $2 million in 2012 to $600 million in 2016, an increase of more than 300 times.
Blockchain technology has received such great attention in a short period of time, mainly because it is seen by many as a breakthrough technology that can transform existing trading models and restructure society from the underlying infrastructure.
Mark Young Jani, Karim Lahani published an article entitled "The Truth About Blockchain" in the Harvard Business Review, which systematically summarizes the operation of the blockchain. The blockchain itself is an open source distributed ledger that efficiently records transactions between buyers and sellers and ensures that these records are verifiable and permanently stored. The ledger can also initiate transactions automatically by setting. Its operating principle can be summarized as: distributed database, peer-to-peer transmission, transparent anonymous letter, irreversibility of records, and computational logic.
ThoughtWorks believes that these characteristics of the blockchain give it a unique advantage in the supply chain finance sector, demonstrating the potential to address all of the problems of existing supply chain finance:
Establish a strong trust relationship with P2P. As a distributed ledger technology, the blockchain is distributed and stored. The data is not maintained by a single centralized organization, and it is not possible to manipulate data according to its own interests. Therefore, it has a strong trust relationship.
Establish a transparent supply chain. The blockchain preserves the complete data, enabling different participants to use consistent data sources rather than decentralized data, ensuring traceability of supply chain information and transparency of the supply chain.
Financial level encryption security. Because the transaction is encrypted and has an immutable nature, the ledger is almost impossible to suffer.
Personalized service. The programmability of the blockchain itself can essentially meet the individual needs of various consumers.
Auditability. A reliable audit trail can be performed by recording the identity information for each data change.
Blockchain is a fundamental technology – it has the potential to create new technological foundations for the economic and trading systems of the supply chain financial industry. What is certain is that blockchain technology will profoundly change the business operations of the supply chain financial industry, and this change is far greater than the changes in the supply chain industry. Blockchain applications are not only a challenge for traditional business models, but also an important opportunity to create new businesses and streamline internal processes.
The Santander InnoVentures Fund predicts that by 2022, banks using blockchain technology can save up to $20 billion annually. The World Economic Forum also predicts that by 2017, 10% of global GDP may be stored on the blockchain platform.
V. Opportunities and scenarios for blockchains for supply chain finance
The characteristics and advantages of the blockchain can help us solve problems in an innovative way and promote the reshaping of the supply chain financial value chain. These innovative applications are ever-changing. Perhaps now, there are many applications that we can hardly imagine and predict. We try to describe the opportunities that blockchains collide with supply chain finance from the following four perspectives.
Opportunity 1: How can the blockchain improve the transparency of the entire industry?
RFID-like technologies have long been applied to increase the transparency of the supply chain, and blockchains ensure transparency and security of the mapping of items from the physical world to the virtual world. The blockchain registers the transfer of goods on the ledger as a transaction to determine the parties involved in the production chain management, as well as the origin, date, price, quality and other relevant information of the product. Because the ledger presents a decentralized structure, it is impossible for either party to own the ownership of the ledger and to manipulate the data for personal gain. In addition, because the transaction is encrypted and has an immutable nature, the ledger is almost impossible to be compromised.
This is of great significance to supply chain finance. The entire supply chain financial enterprise will reassess the risk control model accordingly. It is clear that due to the increase in overall transparency, industry risks will be greatly reduced and all parties will benefit from it.
The blockchain provides a real-time, reliable view of the transaction status for the supply chain, which effectively enhances transaction transparency, which will greatly facilitate intermediaries to lend on the basis of commonly used financial instruments such as invoices and inventory assets. The value of the mortgaged assets will be updated in real time based on real time, which will ultimately help to build a more reliable and stable supply chain financial ecosystem.
|
At present, there have been precedents for trying to improve the supply chain management by using blockchain technology. For example, IBM introduced a service that allows customers to test blockchains in a secure cloud environment and track high-value goods through a complex supply chain. Blockchain startup Everledger is using the service, hoping to use blockchain technology to drive transparency in the diamond supply chain; London's blockchain startup Provenance is committed to providing users with an online platform that enables brands to track products. The origins and history of materials, materials, and products; BlockVerify is also a London-based startup that uses blockchain technology to increase industry transparency and counter product counterfeiting; Skuchain is developing for B2B trading and supply chain financial markets Based on supply chain products; Fluent is working towards “profit in the blockchain chain for supply chain management in the area of ​​major financial modulesâ€.
Opportunity 2: How does the blockchain reduce the overall transaction chain financial transaction costs?
Another area full of potential blockchain applications is to reduce transaction costs. Blockchain technology can bridge the trust gap between different trading entities, when both companies send high-value and high-volume goods, such as iron ore, internationally. A is the shipper and B is the receiver. The parties agree to pay after 30 days of arrival. Party A finds the intermediary financial A to provide supply chain financial services, and B adds credit to it.
In this case, both A and B companies, as well as intermediary financial institutions A and B, are facing unpredictable transportation risks. Now we are trying to circumvent the above risks by signing complex paper documents: the parties must manage the agreement between the shipper’s intermediary financial institution and the recipient’s intermediary financial institution, while also managing the value of the goods and the shipping method. A large number of agreements. Most of the time, we need the original contract document to verify the authenticity of the information.
Using the blockchain application, companies can put all the documents on the blockchain, and based on the blockchain's operating mechanism, the data cannot be changed. In the event of a problem, the party can quickly locate a particular version of the contract document on a particular date via blockchain technology, which is critical to handling disputes. All documents on the blockchain provide full and equal access to everyone, and participants have quick access to target materials, and such access is based on a high degree of trust and traceability and verifiability for all transactions. In fact, the blockchain contains all the necessary components that are critical to supply chain finance: time stamping, irreversibility, and traceability.
|
Once the contract documents are sent and received, the company can pay through the smart contract on the blockchain. The parties to the transaction may agree in advance on the penalty clause of the contract. For example, “When the condition X is satisfied, Party B will pay N to A.†In this way, the blockchain is also realized while giving more personalized services to both the borrower and the lender. The exchange of documents and the exchange of values.
Barclays has tested this possibility. In September 2016, they completed the first field trial of blockchain-based supply chain finance; another example was the agricultural cooperative Ornua and the Seychelles Trading Company (a food product distributor) based on blockchain completion. Butter trade-related documents, although their payments are still “traditionalâ€, use blockchain exchange documents to reduce trade time from 10 days to a few hours. Others are also trying. HSBC and Bank of America Merrill Lynch are using the Linux Foundation's Hyperledger platform to conduct similar experiments and tests in the field of heavy metal trade finance.
Opportunity 3: How does the blockchain create a new business model?
Blockchain technology is not just a technological change, it will ultimately affect contracts, transactions and their records in the supply chain financial transactions, and thus change the current business model. We believe that with the removal of trust barriers and transparent transactions, the blockchain will lead to a true supply chain financial platform.
The new supply chain financial platform, the main players include the platform itself, factoring institutions, intermediary financial institutions, enterprises, individuals and even algorithm companies. The supply chain financial platform is responsible for providing supply chain information, customer information, and other basic services similar to hydropower; third-party intermediaries can integrate based on platform information to provide more customized supply chain financial services, which will be more refined and personalized. Turn.
For example, in the traditional sense, we can mortgage accounts receivable. In the future supply chain financial platform, we can subdivide accounts receivable and establish financial models according to different node states to generate different financial products. At the same time, with the enhancement of traceability in the future, all financial models will update the data according to the real-time status of the supply chain, and continuously evaluate the underlying assets or borrowers. Algorithm companies can develop financial models based on API interfaces provided by the platform and sell them to third-party financial institutions and factoring companies.
|
In the end, the blockchain will enhance the liquidity of mortgage assets in the market, improve the most commonly used supply chain financial instruments, such as factoring, procurement financing, supplier management inventory financing, etc., and provide opportunities for deep financing. Promote a new business model - supply chain finance as a service.
Opportunity 4: How does the blockchain simplify the trading process and enhance the customer experience?
Imagine such a scenario:
Li Lin runs a gold jewelry store in Beijing. Before the arrival of the sales season in the gold jewelry market, as a downstream terminal shop, she wants to pick up the goods in advance. She has tight funds, but as the owner of the terminal store, she knows that this season is the goods. After selling out, she can make a big profit. She finds the supply chain financial platform. The platform virtual assistant provides her with a variety of financial options through the touch screen (such as through the brand's guarantee or counter-guarantee credit enhancement measures to the platform to obtain financing). Borrowing), all the programs are tailor-made for Li Lin, because third-party financial institutions have already learned enough details about Li Lin’s personal and business information through the API interface provided by the platform, such as credit records, violation records, punishment information, etc. . All of the above information is stored through the blockchain, which also ensures that Li Lin's personal information will not be disclosed. At the same time, Li Lin can also get the credit rating information of her external organization based on Li Lin's real-time data mapping in the blockchain.
Li Lin selects the best option through the touch screen. The touch screen reads her fingerprint and the system verifies her identity through the blockchain. After the transfer, the financial institution's bank account is transferred to Li Lin's bank account. Next, the system sets up a monthly direct transfer from Li Lin's bank account to the lending financial institution. These actions are triggered by smart contracts.
One day a few months later, the gold jewelry purchased by Li Lin was lost in transit. The smart sensor installed on the transport outer box triggered the loss notification through the blockchain. The factoring company and the intermediary financial institution received the lost information in the first time. And informed Li Lin to go to the factoring agency. On her way to the factoring agency, she was very worried, not knowing how to handle the claim and refund, and how these would affect her repayment contract. When she arrived at the factoring agency, Li Lin was surprised to find that the claim had been submitted through the blockchain and the factoring company had approved the claim.
This example shows us how blockchain technology can enhance the user experience, and as long as we pay attention, we will find many similar application scenarios.
Finally, technology and scenarios are important drivers for the development of the Internet and IT industries. We believe that in the future, as the blockchain continues to enrich and practice in the supply chain financial application scenarios, it will eventually overturn the entire supply chain financial industry.
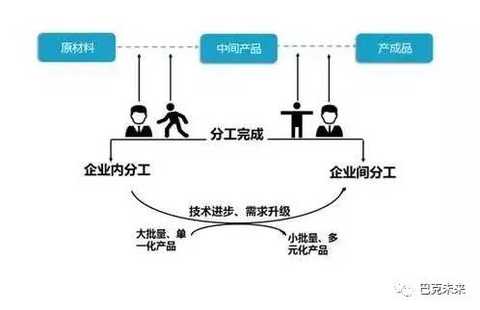
First, supply chain finance
Supply chain finance emphasizes the special relationship between the upstream and downstream member companies competing and cooperating with each other. It is stated that who has the competitive advantage who has the right to speak and who will make the trading conditions and habits. The special relationship is that the industry's characteristics are formed from the original raw materials, through processing, manufacturing, and transportation to the entire chain of the final consumer. Under such circumstances, financial institutions understand the upstream and downstream bargaining power and industry trading characteristics, and provide comprehensive, diversified and customized financial products or services through risk assessment to meet the financial needs of member companies on the chain. .
|
01 Supply Chain Finance 1.0
Based on manual credit approval
The model of supply chain finance is generally referred to as “1+Nâ€. According to the credit support of the core enterprise “1â€, the bank completes the credit guarantee support for the “N†of a small and medium-sized micro enterprise. Supply Chain Finance 1.0 Bank credit relies on the credit of the core factory to alleviate the bank's credit risk to its upstream suppliers or downstream distributors. It adopts manual credits and negotiates on a case-by-case basis.
02 Supply Chain Finance 2.0
Taking the direct link of bank and enterprise as the core
Supply Chain Finance 2.0 is centered on direct banking and business. The core enterprise adopts the automated ERP to manage the supply chain to reduce the inventory cost and respond to the customer's demand in time. At this time, in order to improve the service competitiveness, the bank has reached an agreement with the core enterprise on the “bank-enterprise direct connectionâ€, which is supported by the core enterprise. In addition to relying on the credit of the core enterprise, the bank can grant credit to upstream suppliers and downstream distributors, and can also achieve the purpose of mass acquisition.
03 Supply Chain Finance 3.0
Focus on the three-in-one platform
Supply Chain Finance 3.0 is centered on a three-in-one platform. Supply Chain Finance 3.0 is based on the platform, integrating business flow, logistics, and capital flow into a three-in-one information platform. Banks hold transaction information of all member companies on the supply chain, and are encouraged by the "Internet +" thinking mode. The bank's constant innovation or reform of the business model broke the 28th law, allowing banks to target 80% of the small and medium-sized customers. Thanks to advanced Internet technology support, bank operation costs and risk management costs can be significantly reduced.
Second, the bottleneck facing the supply chain financial promotion
Domestic supply chain finance 3.0 "N+N" from the "1+N" business model of supply chain finance 1.0 has been around for more than a decade. According to IBM research results, about 75% of supply chain financial products are in stock.èžèµ„与预付款èžèµ„,银行ä»å±€é™äºŽä¼ 统的抵押贷款æ€ç»´;然而ä¿ç†ä¸šåŠ¡ä»…å 25%,银行ä»æ— 法回归ä¾æ‰˜è´¸æ˜“èžèµ„具有自å¿æ€§çš„ç‰¹æ€§æŽˆä¿¡ï¼Œç®€è€Œè¨€ä¹‹ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œæ— æ³•ä»…ä»¥ä¹°æ–¹è¿˜æ¬¾åšä¸ºç¬¬ä¸€è¿˜æ¬¾æ¥æºè¿›è¡ŒæŽˆä¿¡ï¼Œè¿½ç©¶å…¶åŽŸå› å°±æ˜¯é£Žé™©è€ƒè™‘ã€‚å› ä¸ºé“¶è¡Œåœ¨ä¾›åº”é“¾é‡‘èžä¸çš„风险管ç†ï¼Œæ˜¯ä¾æ‰˜ç€æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„信用,垂直的对其上游供应商与下游ç»é”€å•†æŽˆä¿¡ï¼Œä¸ºç¡®ä¿é“¶è¡Œå€ºæƒï¼Œé“¶è¡ŒæŽ¨å¹¿ä¾›åº”链金èžä¸šåŠ¡é¢ä¸´ä»¥ä¸‹ç“¶é¢ˆ:
授信对象的局é™æ€§
由于全国å¾ä¿¡ç³»ç»Ÿå°šä¸å®Œå¤‡ï¼Œä¾›åº”链上的ä¸å°æˆ–å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šå˜åœ¨ä¿¡æ¯ä¸å¯¹ç§°ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œæ— æ³•ç›´æŽ¥å¯¹å…¶æŽˆä¿¡ï¼Œå› æ¤é“¶è¡ŒæŽˆä¿¡æ˜¯ä¾æ‰˜ç€æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„信用,ä¸è®ºæ˜¯æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šå¯¹ä¸Šæ¸¸ä¾›åº”商的最终付款责任,或是对其下游ç»é”€å•†çš„æ‹…ä¿è´£ä»»æˆ–è°ƒèŠ‚é”€å”®ï¼Œçš†ä»¥æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„信用为æ æ†è¡ç”Ÿå‡ºæ¥çš„授信。银行除了需è¦æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šé…åˆå¤–,银行也åªèƒ½å±€é™äºŽæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„一级供应商或一级ç»é”€å•†(å³ä¸Žæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šç›´æŽ¥ç¾çº¦çš„供应商与ç»é”€å•†),至于二级以上的供应商与ç»é”€å•†ï¼Œåˆ™å› ä¸ºä¸Žæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šæ— 直接采è´æˆ–销售åˆçº¦ï¼Œæ‰€ä»¥é“¶è¡Œæ— 法æä¾›èžèµ„需求。
科技整åˆçš„å±€é™æ€§
æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šè™½èƒ½æ»¡è¶³é“¶è¡Œå•ç‹¬æŽˆä¿¡çš„æ ‡å‡†ï¼Œä½†å…¶è‡ªèº«çš„ç§‘æŠ€ç³»ç»Ÿï¼Œæ˜¯å¦èƒ½å°†ä¾›åº”链æ¡ä¸Šçš„上ã€ä¸‹æ¸¸æˆå‘˜ä¼ä¸šäº¤æ˜“讯æ¯æ•´åˆä¸€èµ·ï¼Œä½¿å¾—链上的采è´ä¿¡æ¯ä¸Žé”€å”®ä¿¡æ¯é€æ˜Žä¸”å¯ä¿¡èµ–,这决定了银行是å¦èŽ·å¾—对称的信æ¯è€Œæ”¯æŒå¯¹ä¸Šä¸‹æ¸¸æˆå‘˜ä¼ä¸šçš„授信。å¦å¤–,交易信æ¯çš„真伪如何验è¯?交易信æ¯æ˜¯å¦è¢«ç¯¡æ”¹ç‰ç‰é—®é¢˜ä¹Ÿåˆ¶çº¦ç€ä¾›åº”链金èžä¸šåŠ¡çš„推广。
交易全æµç¨‹ä¸é€æ˜Ž
供应链金èžæ˜¯æ•´åˆäº†å•†æµã€ç‰©æµä¸Žèµ„金æµï¼Œå¦‚果线上的商æµä¸Žçº¿ä¸‹çš„物æµæ— 法达到信æ¯é€æ˜Žä¸”全程å¯è§†ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œå¯¹æŠ¼å“的控货æƒå¯èƒ½äº§ç”Ÿé£Žé™©ç–‘虑,也会制约供应链金èžä¸šåŠ¡çš„å‘展。
三ã€åŒºå—链打通供应链金èžçš„瓶颈
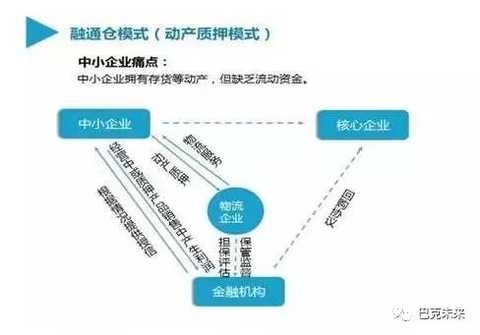
基于风险管ç†çš„è€ƒè™‘ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œä»…æ„¿å¯¹æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šæœ‰åº”收账款义务的上游供应商(一级供应商)æä¾›ä¿ç†ä¸šåŠ¡(应收å¸æ¬¾èžèµ„)或是对其直接下游ç»é”€å•†(一级ç»é”€å•†)æ供预付款èžèµ„或å˜è´§èžèµ„ï¼Œå› ä¸ºé“¶è¡Œä¿¡èµ–æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„控货能力或是调节销售能力。å之,除了一级供应商或ç»é”€å•†å¤–,银行一般ä¸æ„¿ç›´æŽ¥æŽˆä¿¡ã€‚å¦å¤–,在金èžå®žé™…æ“作上,银行éžå¸¸å…³æ³¨åº”收å¸æ¬¾å€ºæƒâ€œè½¬è®©é€šçŸ¥â€çš„法律效力,所以都会è¦æ±‚ä¸€çº§ä¾›åº”å•†æˆ–æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šç¾å›žâ€œå€ºæƒè½¬è®©åŒæ„书â€ï¼Œå¦‚æžœä¸€çº§ä¾›åº”å•†æˆ–æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šæ— 法ç¾å›žï¼Œä¹Ÿä¼šé€ æˆé“¶è¡Œä¸æ„¿æŽˆä¿¡ã€‚
|
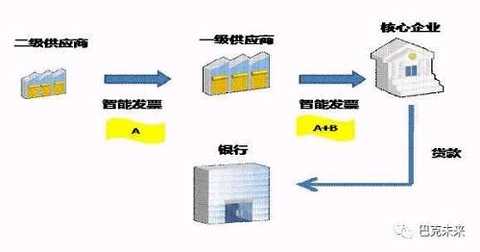
若银行在区å—链技术支æŒä¸‹ï¼Œå¼€å‘一个供应链金èž'智能ä¿ç†â€ä¸šåŠ¡åº”用系统,æ供给所有供应链上的æˆå‘˜ä¼ä¸šä½¿ç”¨ï¼ŒäºŒçº§ä¾›åº”商利用“智能ä¿ç†â€ç³»ç»Ÿå°†å¼€ç»™ä¸€çº§ä¾›åº”商的å‘票上记载ç€è¯¥åº”收å¸æ¬¾å·²è½¬è®©ç»™æŸé“¶è¡Œçš„ç¼–ç (ç¼–ç A),å‘布在区å—链上,一级供应商在æ¤å‘ç¥¨çºªå½•ä¸Šæ·»åŠ å…¶ä»–å¿…è¦çš„ç¼–ç (ç¼–ç B)之åŽè¿žåŒåŽŸè½¬è®©ä¿¡æ¯å˜æˆç¼–ç A+B,å†å‘布在区å—链上。ä¾åˆåŒæ³•ç¬¬79æ¡å’Œç¬¬80æ¡è§„定,æ¤æ™ºèƒ½å‘票已达到债æƒè½¬è®©æ³•å¾‹é€šçŸ¥çš„æ•ˆæžœï¼Œæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šå½“货款到期时ä¾æ³•åº”直接将款项付给银行(如下图)。æ¤å¤–,银行也å¯ä»¥åˆ©ç”¨â€œæ™ºèƒ½ä¿ç†â€ç³»ç»Ÿè¿½æº¯æ¯ä¸ªèŠ‚点的交易,勾画出å¯è§†æ€§çš„交易全æµç¨‹å›¾ï¼Œæ‰€ä»¥åŒºå—链技术为推广供应链金èžâ€œä¿ç†â€ä¸šåŠ¡åˆ°æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šçš„二级以上的供应商æ供良好的基础。
|
银行对ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šæˆ–å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šé™¤äº†æ‹…心其还款能力外,也关注交易数æ®ä¿¡æ¯çš„真实性。供应链金èžä¸šåŠ¡å®žé™…æ“作ä¸ï¼Œæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šæ˜¯ä»¥å…¶ERP为ä¸å¿ƒåŒ–的模å¼ä¸²è¿žä¸Šæ¸¸é‡‡è´ä¿¡æ¯ä¸Žä¸‹æ¸¸é”€å”®ä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œæ‰€ä»¥é“¶è¡Œå¿…å®šè°ƒæŸ¥æ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šæ‰€ç”¨çš„ERP系统的生产商,由于国际或国内大厂生产的ERP系统结构较为å¤æ‚,交易信æ¯è¾ƒä¸æ˜“被篡改,银行对其信æ¯çš„ä¿¡ä»»åº¦æœ‰æ‰€å¢žåŠ ã€‚å°½ç®¡å¦‚æ¤ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œä»ç„¶æ‹…å¿ƒæ ¸å¿ƒä¼ä¸šä¸Žä¾›åº”商或ç»é”€å•†å‹¾ä¸²ç¯¡æ”¹äº¤æ˜“ä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œæ‰€ä»¥æŠ•å…¥äººåŠ›ä¸Žç‰©åŠ›åå¤éªŒè¯äº¤æ˜“ä¿¡æ¯çš„真伪。å观区å—链具有一致性ã€å¯æº¯æ€§å’ŒåŽ»ä¸å¿ƒåŒ–çš„ç‰¹ç‚¹ï¼Œå› æ¤å¯å°†ä¾›åº”链上所有的交易数æ®è®°å½•åˆ†æ•£åœ¨æ‰€æœ‰ç»“点上的数æ®åº“,且区å—链上的数æ®éƒ½å¸¦æœ‰æ—¶é—´æˆ³ã€ä¸é‡å¤è®°å½•ç‰ç‰¹æ€§ï¼Œå³ä½¿èƒ½ç¯¡æ”¹æŸä¸ªèŠ‚点的交易数æ®ï¼Œä¹Ÿæ— 法åªæ‰‹é®å¤©ï¼Œæ‰€ä»¥åŒºå—链解决了银行对信æ¯è¢«ç¯¡æ”¹çš„疑虑。
|
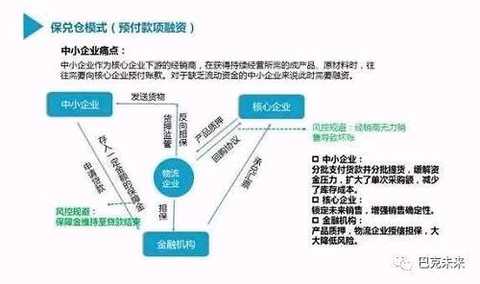
å¦å¤–,银行在æ“作供应链金èžçš„“å˜è´§èžèµ„â€å’Œâ€œé¢„付款èžèµ„â€çš„è´·åŽç®¡ç†ï¼Œå¿…é¡»ç¼–åˆ—ä¸€å®šäººæ•°çš„â€œå·¡æ ¸å‘˜â€ï¼Œæ¥æ ¸å®žæŠ¼å“是å¦å˜åœ¨ä¸ŽæŠ¼å“价值是å¦å‡æŸç‰å·¥ä½œï¼Œé€ æˆé“¶è¡ŒæŠ•äººå¾ˆå¤šçš„äººåŠ›ä¸Žç‰©åŠ›ï¼Œå¢žåŠ é“¶è¡Œæ“作æˆæœ¬ï¼Œè‡´ä½¿ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šæˆ–
å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šèžèµ„æˆæœ¬æ高。如果银行利用区å—链“智能资产â€æ¥ç®¡ç†æ‰€æœ‰ä¾›åº”链上交易押å“,ä¸ä½†èƒ½å¤ŸéªŒè¯æŠ¼å“的真实性,åŒæ—¶ä¹Ÿå¯ä»¥ç›‘控押å“的转移,如æ¤ä¸€æ¥ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œå¯ä»¥èŠ‚约投人大é‡çš„äººåŠ›å·¡æ ¸ä¸Žç›˜ç‚¹æŠ¼å“,也å¯ä»¥å‡å°‘æ“作风险和é™ä½Žä½œä¸šæˆæœ¬ã€‚
|
银监会举行的“ä¸å›½é“¶è¡Œ601988 ,è‚¡å§ä¸šç›˜ç‚¹'å二五'展望'å三五"çš„æ–°é—»å‘布会,æ示银行业应该“注é‡åˆ›æ–°å’Œæ”¹é©â€åŠâ€œæ³¨é‡æ™®æƒ 金èžçš„å‘展â€ï¼Œç®€è€Œè¨€ä¹‹ï¼Œå°±æ˜¯é¼“励银行业多用“互è”网+''科技手段和æ€ç»´æ¨¡å¼æ¥åˆ›æ–°å’Œæ”¹é©é‡‘èžï¼Œå¹¶å°†å®žæƒ åŠèµ„æºç¡®å®žåœ°è½åˆ°ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šæˆ–å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šç‰å®žä½“产业,真真æ£æ£åœ°å‘å±•æ™®æƒ é‡‘èžã€‚供应链金èžå°±æ˜¯çž„准ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šæˆ–å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šçš„金èžè§£å†³æ–¹æ¡ˆï¼Œå›½å†…银行业推行å余年,虽具规模,但对ä¸å°ä¼ä¸šæˆ–å°å¾®ä¼ä¸šèžèµ„需求,ä»æ˜¯æ¯æ°´è½¦è–ªï¼Œå½’æ ¹ç»“åº•å…¶ä¸åŽŸå› 就是风险管控与æ“作æˆæœ¬è€ƒè™‘。
|
如今金èžç§‘技å‘展迅猛,国外知å银行趋之若鹜纷纷投资æˆç«‹åŒºå—é“¾å®žéªŒå®¤ï¼Œå°±æ˜¯å› ä¸ºåŒºå—链真æ£çš„能将交易数æ®ï¼Œå®žçŽ°å¼€æ”¾ã€ä¸€è‡´ã€çœŸå®žéªŒè¯ä¸”ä¸èƒ½ç¯¡æ”¹ï¼Œé“¶è¡Œèƒ½æ›´å¥½åœ°ç®¡æŽ§é£Žé™©å’Œå¤§å¹…é™ä½Žé“¶è¡Œä½œä¸šæˆæœ¬ã€‚区å—链技术未æ¥çš„å‘展与应用,å¯èƒ½æˆä¸ºé“¶è¡ŒæŽ¨å¹¿ä¾›åº”链金èžä¸šåŠ¡æœ€ä½³çš„解决方案,银行å¯ä»¥ä¸å†å±€é™æŠ¼å“èžèµ„,而æ¸æ¸è½¬å‘çœæ—¶ã€ä¸éœ€æŽ§è´§å’Œä½Žæ“作æˆæœ¬çš„ä¿ç†ä¸šåŠ¡ï¼ŒæœåŠ¡æ›´å¤šçš„客群,真æ£ä½¿é“¶è¡Œä¸šè½å®žâ€œæ³¨é‡åˆ›æ–°å’Œæ”¹é©â€åŠâ€œæ³¨é‡æ™®æƒ 金èžçš„å‘展â€ç›®æ ‡ã€‚
本文首å‘于微信公众å·ï¼šä¸å›½æŠ•è¡Œä¿±ä¹éƒ¨ã€‚ The content of the article belongs to the author's personal opinion and does not represent the position of Hexun.com. Investors should act accordingly, at their own risk.
(Editor: Yue Right HN152)
The style of denim skirt allows you to wear a variety of styles when choosing a outfit. Thicker fabrics are better in spring, and different styles are combined to change a variety of styles. Celebrities and fashionistas have a preference for it. The simple combination of items that go out on the street every day will give you a proper concave shape. Take a look at the following styles of item collocation to help you choose the right item to go out on the street.
Denim Skirt For Women,Denim Midi Skirt,Stretch Denim Skirt,Black Denim Mini Skirt
Dongguan Arrow Dragon Clothing Co.,Ltd. , https://www.jljeansfactory.com